“The idea of ‘Smart Investment Strategies to Build Long-Term Wealth’ intimidates us in an age of instant gratification and short attention spans. Yet it is the foundation of financial security and of freedom itself. Growing rich doesn’t happen overnight; it requires time and strategic planning.
This piece will reveal “smart investment strategies” that will help you “build long-term wealth”. We’ll talk basics, investment building blocks, and basic habits to develop for a lifetime of financial prosperity. By implementing these techniques, you’ll be able to lay the foundation for a brighter financial future and start building wealth.
1. The Basis for Smart Investment Strategies to Build Long-Term Wealth
Mindset, Goals, and Discipline
1. Start Early (The Power of Compounding):
- Detail: The younger you start investing, the longer your money will enjoy time to compound and grow at an exponential rate, in which the money you earned will make you even more money.
- Why it’s beneficial: Even modest, regular investments early in life can outperform larger investments later in life.
2. Define Clear Financial Goals:
- Detail: What is it you are saving for? Retirement, a child’s education, a home, financial independence? Concrete goals bring focus and inspiration.
- Why it’s beneficial: Goals drive how much to invest as well as where to and for how long. Learn how to set financial goals from Ally Bank.
3. Plan and Save: Create a No-Spend Budget and Save Regularly
- Detail: Know your ins and outs. Budgeting helps you know where to save and have room in your cash flow to contribute on a regular basis.
- Why it’s beneficial: Regular saving is the gasoline in your investment engine. Automate savings to build discipline.
4. Save for Emergencies: Build and Maintain an Emergency Fund:
- Detail: Before going all in, establish a liquid fund (3–6 month’s worth of living expenses) in a savings account.
- Why it’s beneficial: It can keep you from having to sell long-term investments at a loss in the event of a surprise financial crisis.
2. Principles of Smart Investing
Strategic Approaches for Sustainable Growth
1. Diversification (Don’t Bet the Farm on One Horse):
- Detail: Diversify your investments across asset classes (equities, debt, real estate, and gold), sectors and geography.
- Why it’s beneficial: Mitigates risk; if one investment does badly, others may do well, so the good and the bad help to balance out your portfolio.
2. Invest for the Long Term (Don’t Try to Time the Market)
- Detail: Emphasis on holding quality investments for years, even decades. Avoid the temptation to trade on the basis of short-term market movements or “news.”
- Why it’s beneficial: It is notoriously difficult to time the market. Investing for the long run can help you harness the gains of the overall market and is the best way to ride out the market’s inevitable ups and downs.
3. Dollar-Cost Averaging (SIP – Systematic Investment Plans in India)
- Detail: Invest a set dollar amount at set intervals (say monthly) irrespective of prices in the market. You buy more units when prices are low and fewer when prices are high.”
- Why it’s beneficial: Smooths the average purchase price over time – reducing risk and taking emotion out of the equation. Works wonders for mutual funds in India.
4. Rebalance Your Portfolio Periodically:
- Detail: As the performance on each of the investments changes over time, your asset allocation may change as well. That process of selling some of the outperforming assets and buying more of the underperforming assets to return to your target allocation is known as rebalancing.
- Why it’s beneficial: It helps you keep your desired risk level and can make you “buy low and sell high”.
5. Focus on Low-Cost Investments
- Detail: If high fees (management fees, expense ratios) are plucking too many of your feathers, then your long-term returns can be significantly compromised. Choose from low-cost index funds, ETFs, or direct plans of mutual funds.
- Why it’s smart: Even small differences in fees can result in huge disparities in wealth accumulated over decades.
3. Long-Term Growth Investment Workhorses

Where to Stash Your Money, Besides Under Your Bed, for the Next Emergency
Stocks (both individual stocks and equity mutual funds):
Detail: Provide the greatest long-term growth attitude solution. These can be largely individual stocks (blue chip, growth, dividend-paying ones) or even diversified equity mutual funds/ETFs.
Consideration: Greater volatility, but necessary for wealth generation.
Debt Instruments (Bonds & Debt Mutual Funds)
- Detail: Offer security and some stable income. Bonds of the government, of corporations and of mutual funds full of debt.
- Consideration: Lower returns compared with stocks, but important for portfolio stability and capital preservation.
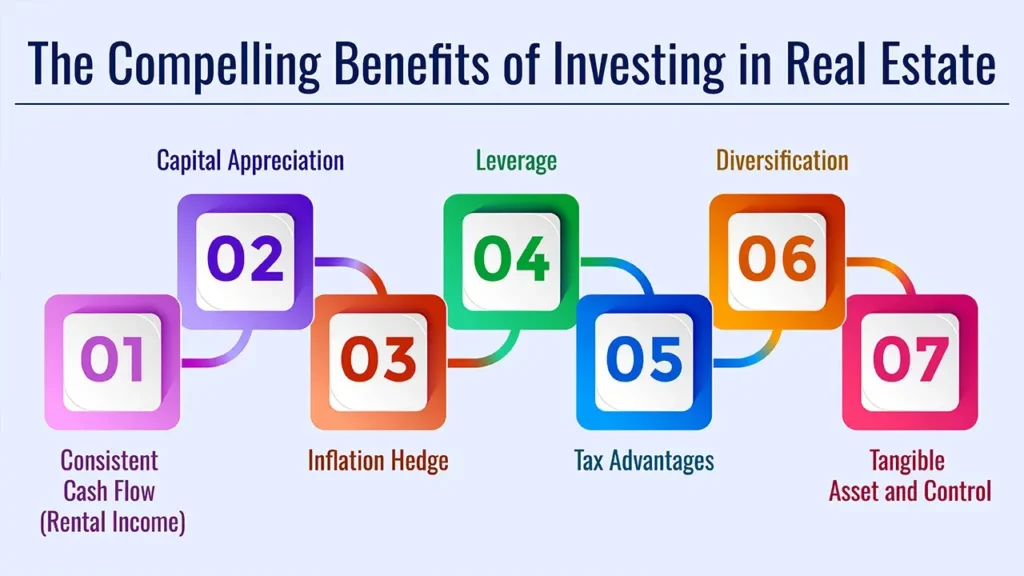
Real Estate
- Detail: Can be cashflow and growth. You could own the property outright, own shares (such as in real estate investment trusts, or REITs), or own fractions.
- Consideration: Illiquid, high entry cost to direct ownership, but potentially an inflation hedge.
Gold
- Detail: Can act as a hedge against inflation and economic insecurity. Can be invested in physical gold, gold ETFs or sovereign gold bonds.
- Consideration: Doesn’t make money, but diversifies and adds safety.
Policies focused on retirement (NPS, PPF, EPF, etc. in India)
- Detail: Tax-friendly, long-term, compounding schemes run by the government or under government supervision in your country.
- Consideration: Long lock-ins, great for retirement planning.
4. Habits and Pitfalls to Avoid
Developing A Mindset And Steering Clear From Mistakes
Good Habits: Always learning personal finance, revisiting/marking your portfolio consistently, disciplined purchasing, and adding more to your investments with an increase in income.
Avoid these common pitfalls:
- Emotional Investing: Allowing decisions to be driven by fear or greed.
- Pursuing Hot Tips/Fads: Making speculative investments in unproven assets without doing any of the due diligence.
- Not heeding due diligence: not knowing what you are investing into.
- Too Much Debt: Interest on debt can cancel out gains from investments.
- Over-Leveraging: Over-borrowing to invest, and so increasing losses.
- Hyper-Focused on Returns: Not considering risk, fees, or liquidity.
Conclusion
In short, “smart investment strategies to build long-term wealth” are premised on having goals, systematically saving and investing, and disciplined asset allocation in multiple classes. His mantra is to build “long-term wealth”, which he says is a journey that demands patience, persistence, and a desire to learn.
With these fundamental approaches and pitfalls in mind, you will be prepared to successfully navigate the investment world and provide a financially sound future for you and your loved ones!
Call to Action
You should begin today, even if you invest small amounts, and also look at taking the advice of a SEBI-registered financial advisor for customized advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How much do I need to invest to become wealthy over the long run?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Begin with what you can afford to do on an ongoing basis, no matter how modest that amount may be. The trick is to act consistently and as early as possible.
A good rule of thumb is to set aside at the very least 10-20% of income, bumping it up a bit as your income increases.
2. Is the stock market too dangerous when it comes to building long-term wealth?
Markets have been known to make people rich overnight or poor in just minutes; in the short term, it is very volatile, but over a long period of time, historically, equities have given the best returns – they have beaten inflation and other asset classes.
This risk is greatly diminished by diversification, focusing on quality companies/funds and taking a long-term view.
3. How much does inflation matter in long-term wealth building?
It’s inflation and stripping your money of its purchasing power. Intelligent investment strategies seek to produce returns that are higher than inflation so that your money grows in real terms.
Assets such as stocks and real estate tend to be good hedges against inflation.