How can you protect yourself and your loved ones against financial shocks, given the constant barrage of unpredictable events that seem to be happening everywhere? The answer frequently comes from grasping “what is insurance.”
This article will reveal what is insurance, help you grasp what insurance is really about, showcase the most common types of coverage, and illustrate the priceless peace of mind insurance provides to create a solid financial future.
Simply by understanding a few basic principles about insurance, you can make intelligent choices that protect your assets and maintain peace of mind. I am willing to bet that, whether you are thinking about life, health, or property insurance, you already know the basics of what follows – a knowledge of these basics is that the backbone of financial planning.
Now, let’s head through the realm of insurance and check out how it can become your best friend in financial remedy.
Section 1: What is Insurance? The Core Concept
Definition of Insurance: A Protection Agreement
- Easy to understand: Insurance represents a contract where an individual (policyholder) agrees to pay a fee (premium) to an insurance company (insurer), an in exchange receives a promise to pay his insured sum in case of certain financial losses caused by specific events.
- Risk Reduction: Insurance is a basic form of risk management and the insured’s risk is transferred to pool of people (insured’s customers) who are exposed to similar risk.
Key Terms to Know:
- Premium: The amount you pay (in premium) the insurance company for your policy.
- Policyholder: The buyer of the insurance (it can be a person or an entity).
- Insured: The individual or organization whose risks are being insured.
- Insurer: The firm that provides the insurance.
- Policy: The policy wording, which is the legal agreement containing the terms and conditions.
- Deductible: The sum the policyholder pays with their own money before insurance begins.
- Claim: A request, made in writing for compensation under the policy.
- Sum Assured/Policy Limit: The highest amount the insurance company will pay for a specified loss.
For a foundational understanding of what insurance is and its core principles, refer to Investopedia’s definition of Insurance.
Section 2: Why You Need Insurance?
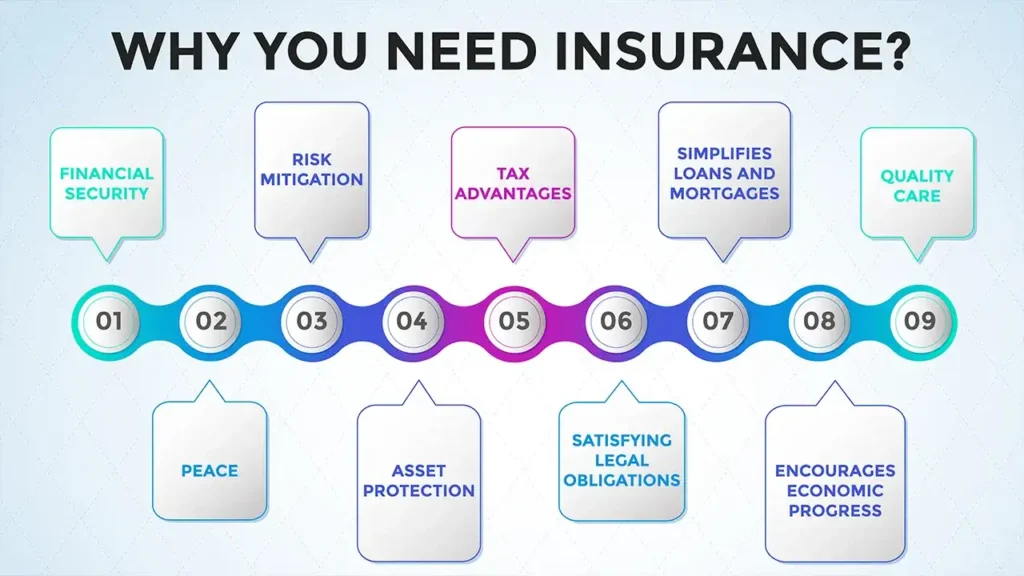
The Many Advantages of Having Insurance
- Financial Security: The ultimate purpose of insurance is to shield you and your family members from awful shocks in the form of devastating economic losses that can otherwise destabilize you if you are hit by diseases, accidents, death or destruction of your possessions.
- Peace: In a world dominated by uncertainty, worldly possessions may be lost, Insurance promises that your loved one keep going on with their life without being bogged down by the fear of what you may lose.
- Risk Mitigation: It shifts certain risks from your side to the insurer side, thus being a security net.
- Asset protection: Insurance protects your wealth (your home, your car, health) against damage or loss.
- Tax advantages: Some types of insurance provide for a tax-free payout and others allow for a deduction when the policyholder pays taxes.
- Satisfying Legal Obligations: Certain types of insurance, such as vehicle insurance, may be a legal requirement.
- Simplifies Loans and Mortgages: Most loans, like mortgages, are made under the condition that they are securitized, so you must get home insurance if you want a mortgage with the bank.
- Encourages Economic Progress: Pooled investment and savings of passengers by insurance companies lead to their investment in the economy which promotes economic progress.
- Quality Care: Medical Coverage provides access to the best possible treatment without draining the savings.
Section 3: Types of Insurance: Covering Every Aspect of Life
Types of Policies:
1. Life Insurance:
Purpose: This fund does offer your beneficiaries monetary relief after you pass away.
Types:
- Term Life Insurance: Protection for a set period of time.
- Whole Life Insurance: Permanent coverage with a cash value component.
- Endowment Plans: Life coverage coupled with savings.
- ULIPs (Unit-Linked Insurance Plans): Unit Linked Insurance Plans Meaning: insurance linked investment.
- Money Back Plans: Regular payouts throughout the policy duration.
2. Health Insurance:
Purpose: Pays for medical-related expenses, such as hospitalisation, visits to the doctor, and medication.
Types:
- Individual Health Insurance: Coverage for one person.
- Family Floater Plans: Everyone in the family can be covered under the same policy.
- Critical Illness Cover: Cover for major health conditions.
- Senior Citizen Plans: Designed for the elderly.
- Group Health Insurance: Coverage provided by an employer for the employees.
- Maternity Insurance: Provides coverage for those all things pregnancy.
3. General Insurance (Non-Life Insurance):
- Vehicle Insurance: Covers damage to your vehicle and damage to third parties.
- Home Insurance: Safeguards your home from perils such as fire, theft, tornado, etc.
- Travel Insurance: This insurance covers things from medical emergencies to lost luggage to trip cancellation while traveling.
- Property Insurance: Generic term for the various types of insurance which cover real property.
- Personal Accident Insurance: Offers reimbursement for injury, disability or death caused from an accident.
- Business/ Commercial Insurance: Offers protection from industry-related risks such as liability and property damage.
Section 4: Choosing the Right Insurance Coverage
Factors to Consider Before Buying Insurance
- Evaluate Your Needs: Decide on the risk you would like to cover, like family members who are dependents, assets or health problems.
- Budget: Determine what you can afford to pay in premiums without placing stress on your finances.
- Sum Assured: Check if the sum assured is sufficient based on your requirements and future expenses.
- Policy Terms and Conditions: Read the fine print, including exclusions and waiting periods.
- Claim Settlement Ratio: Check the reliability of the insurer based on their claim settlement record.
- Customer Service: Consider how accessible and amenable (or not) the insurance company is to answering your questions.
- Advisor vs Online: You choose whether to buy through a broker, agent or directly online.
Conclusion: Invest in Your Protection, Invest in Your Future
In summary, understanding the meaning of insurance, its diverse types, and the profound benefits it offers is essential for anyone looking to secure their financial future. Insurance isn’t simply an expense – it’s as an investment in your peace of mind and financial stability.
Spend some time looking into what your current insurance needs are and if necessary, contact someone who can offer professional advice to ensure that you are properly protected against life’s risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary use of insurance?
The fundamental concept of insurance is to provide a source of recovery in the event of a loss, such that both individuals and organisations can transfer risk of financial ruin to an insurance company in return for regular payments, known as premiums.
What is premium, deductible and sum assured?
The premium is the money an individual pays regularly to an insurance company. The deductible is the price you’re willing to pay out of your own pocket for a covered loss, before your insurance starts to cover the costs.
The sum insured (or policy limit) is the highest amount the carrier will pay for a covered loss.
Is insurance an investment?
Although there are certain insurance types (for eg: ULIPs or endowment plans) which have an investment element to it, insurance is meant for protection against risk first.
Pure protection plans such as term insurance come with no maturity benefit or investment.
Why is it necessary to tell complete truths while purchasing insurance?
Reporting all necessary information accurately is an important requirement in insurance as it is placed on “utmost good faith.”
Withholding or falsifying information may cause your claim to be rejected in future – effectively rendering your policy useless in your hour of need.
Do I need to review my insurance policies on a regular basis?
It makes sense to look over your insurance every year, or when life events like a marriage or a baby happen, you buy a home or a car, or your health takes a turn.
By doing this regularly, you are coming close to guaranteeing that you’re never going to be without sufficient coverage.