Bored of your money just sitting there? Think of it as a friend doing the work for you, growing riches while you sleep. Investing in real estate is a great way to build long-term wealth and financial security.
To help you get started, we have put together a complete a beginner’s guide to real estate Investing that covers the steps needed to begin investing in real estate. From learning how to invest in real estate to finding your first investment property and taking care of it, we’ve got you covered.
Why Real Estate Investing?
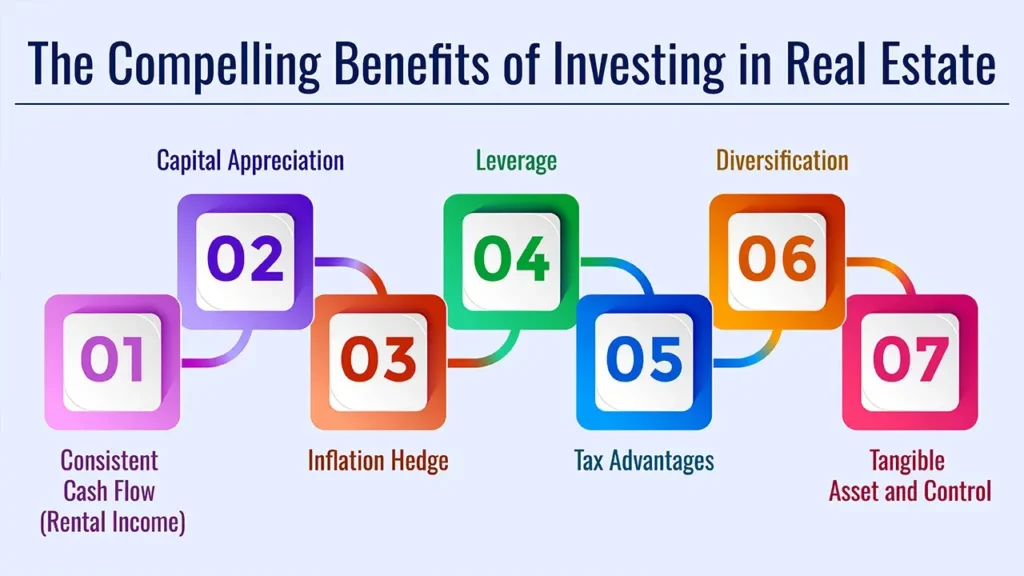
Investing in real estate has some fantastic advantages making it one of the best ways to build wealth! Here are some key advantages:
- Passive Income: Rental properties can create a passive income stream allowing you to earn money while you are off doing other things.
- Appreciation: As your property value generally increases over time, you’ll have a capital gain when you sell.
- Tax Benefits: Real estate investors enjoy a number of tax benefits, such as mortgage interest deductions, property taxes and depreciation.
- Inflation Hedge: Real estate generally increases in value during times of inflation, preserving the purchasing power of your investment.
- Control and tangibility: Real estate which is unlike stock or bond, is a tangible asset that is yours to work on and to improve.
Why Real Estate? The Enduring Appeal of Property
1. Long-term Wealth Building
Real estate has always been one of the most reliable ways to accumulate wealth over the long term. Property tends to increase in value, so your investment has the potential to increase in value as well.
Historically, real estate does extremely well relative to other asset classes over long periods of time, and so it’s a good decision that should provide you with lots of wealth over time.
2. Passive Income Potential
One of the appealing things about real estate investment is the promise of passive income. Through buying rental units, you can make money on a monthly basis with tenants.
This income can be put toward your mortgage payments, property taxes, and maintenance and can also give you an additional cash stream.
3. Inflation Hedge
Real estate is an inflation hedge. If the cost of living is going up, if rents are going up and property values are going through the roof. This is what one calls protecting your investment from the ravages of inflation and choosing wisely for your financial security over the long run.
4. Tax Advantages
There are many advantageous tax benefits to investing in real estate. Mortgage interest, property taxes and certain costs associated with property management can all be written off for investors.
Moreover, depreciation enables you to lower your taxable income, maximizing your cash balance even more. Another tax strategy is the 1031 exchange, which allows you to defer capital gains tax when you sell one property and invest the proceeds in another property. This is likely to be complicated and you may need some professional help.
5. Control and Tangibility
Real estate provides more power being tied to it as an investment, during this period. Property management can be done by you, you can also decide which tenant you want to have, and you can decide if you need to do renovations.
And there’s something about real estate that is a physical, touchable investment, as opposed to something intangible real estate can provide that security other investments can’t.
Before You Start: The Must-Know Fundamentals for Aspiring Investors
Financial Health Check
Before jumping into real estate investing, you need to get a handle on your finances. Here are several factors to keep in mind:
- Debt Management: Understand the difference between good and bad debt. Good debt, such as a mortgage, can help you build wealth, while bad debt, like high-interest credit cards, can hinder your financial progress.
- Emergency Savings: Make sure you have a cushion to cover any unforeseen costs. Having a well-funded emergency fund can keep you off credit in hard times.
- Credit Score: Your credit score is crucial in helping obtain favorable loan terms. Review your credit report for mistakes and if needed work to get your score up.
Setting Clear Goals
Setting clear objectives is crucial to your success in real estate investment. Consider the following:
- What Do You Want to Achieve? Define your goals: so that may be passive income, wealth creation, or even early retirement.
- Short Term Vs Long Term Goals: Classify between what you want immediately with your future. Short-term goals may be buying your first property and long-term ones would be to accumulate a range of real estate properties.
Education is Key
In fact, it really does come down to power in real estate investing. Here are a few places to educate yourself:
- Books: Read books on real estate investing, property management, and market analysis.
- Podcasts: There are podcasts where successful investors talk about their experiences and pundits explain their methodologies.
- Online courses: Sign up for online courses that explain real estate investing in different aspects.
- Mentors: Find other investors, so you can tap into and get advice from as you go through the market.
Assembling Your Team
You will need to develop a solid support system. Consider the following professionals:
- Realtor: Look for a good agent who is knowledgeable about the local market and will assist you in finding the right investment property for you.
- Lender: Know your financing options and identify a lender that can assist you in reaching your goals.
- Legal guidance: Speak with an attorney to make sure you’re making decisions that are informed and within the parameters of local laws.
- Accountant: A great accountant can guide you through tax laws and help make the most of your returns.
- Property Manager: If renting, a property manager will manage tenant issues and maintenance.
Enticing Strategies On How To Invest In Real Estate For Beginners
Rental Properties (Long-Term)
One of the most popular strategies, even among beginners, is investing in rental properties. Here are some of the important factors to keep in mind:
- Residential Properties: You can purchase single-family or multi-family residences. Residential properties experience an unceasing demand as people will always require somewhere to live.
- Pros and Cons: Rental properties can offer a reliable income stream, but also involve hands-on management and the costs of upkeep.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
REITs offer a way to invest in a portfolio of income-generating properties, without the hassle of managing properties yourself.
- Pros and cons: They provide liquidity and diversification, but you may have less control of the properties and their management.
Real Estate Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding platforms (like Fundrise) give you the ability to team up with other investors to fund major real estate developments.
- Pros and Cons: This approach creates a lower barrier of entry to the new investor, by potentially relinquishing some control and giving up some liquidity.
House Hacking
House hacking is when you live in one unit of a multi-unit property and rent out the others.
- Pros and cons: This approach can save a lot on housing costs, but it might make it harder to find privacy.
How to Find Your First Investment Property Location!
Market Research
Do some in-depth market research and learn about some potential investments that look promising. Consider the following factors:
- Population Growth: Find where the population is growing, which can increase demand for housing.
- Employment Growth: A strong employment market can result in increased need for rentals and property values.
- Median Income: Make sure the average median income is conducive to rental rates.
Neighborhood Analysis
Analyze neighborhoods by different factors:
- School Districts: High school districts can have a big impact on property values and who will be drawn to the area.
- Crime: Nobody wants to live in a scary neighborhood!
- High Property Values: Areas with rising property values is the best play to get the best return on your investment.
Property Analysis
Do an in depth analysis of potential properties:
- Cash flow Analysis: Check income against expenses to get positive cash flow.
- Cap Rate, ROI, Gross Rent Multiplier: These are a few of the key metrics you need a basic understanding of to be able to gauge the potential of the property.
- Property’s Condition: Evaluate the house’s condition and what sort of repairs or refurbishment it calls for.
Networking
Get to know some of the more active local agents and investors seeing what off-market properties they have available. Contacts can share information and opportunities that you won’t find out in public.
Financing Your Real Estate Dreams
Traditional Mortgages
Compare the different types of mortgages.
- Conventional Loans: Usually available to borrowers with a higher credit score and down payment, these loans generally have competitive interest rates.
- Loans for first-time homebuyers: These are backed by the government and include FHA loans, which require a lower down payment.
- VA Loans: These loans for veterans often require no down payment and offer favorable terms.
Hard Money Loans
Hard money loans are short-term, high-interest loans used to make fast deals. They can be helpful for investors who want to buy properties in a short amount of time, but they’re also more expensive.
- Private Money Lenders: Loans from people can be more flexible. Just make sure you’ve got some kind of arraignment happening, because we don’t want any insinuations.
- Seller Financing: With seller financing, instead of paying a bank, you will make your payments to the seller, who is financing the purchase. This may be a good alternative if you have problems getting traditional loans.
- BRRRR Method: The BRRRR method (Buy, Rehab, Rent, Refinance, Repeat) is a formula to grow a portfolio. With this method, you can use your equity to purchase other properties.
How To Manage Your Investment – From tenant selection to property maintenance

Tenant Screening
When you’re a landlord, tenant selection is key to success. Consider the following:
- Credit: Check that the tenants have a strong credit rating.
- Check for Background: Research tenants’ rental history and criminal history.
- Fair Housing Laws: Know what you can, can’t do to prevent discrimination as a landlord.
Lease Agreements
A detailed lease agreement is a must to protect your investment. Key clauses to include:
- Term: Term indicate the length of the lease and options to renew it.
- Rent Payment Notes: Specify methods of payment and due dates.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Include an agreement on who will be responsible for any maintenance tasks.
Rent Collection and Evictions
Create a system for collecting rent, and be familiar with eviction laws. Get to know local laws so that you don’t break any.
Property Maintenance and Repairs
You need to maintain the value of your property. Consider the following:
- Scheduled Maintenance: Set up regular check ups so that you avoid expensive repairs.
- Repairs: Be ready to solve any unexpected issues rapidly with a well-thought-out emergency-response process.
Hiring a Property Manager (Optional)
If you have multiple properties, or don’t have the time to manage them on your own, consider hiring a property manager. Find someone who is experienced and has a good reputation.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Vacancy Periods
Empty dwellings affect your cash flow, as well as liberty time. To speed up this process, you can do the following:
- Advertise Your Property: List your place online and on social media to find potential tenants.
- Provide an Inducement: If possible, offer discounts or inducements to secure tenants faster.
- Problematic Tenants: Dealing with them can be a headache. So to mitigate the risks that come with renting, screen your tenants meticulously and set clear leases.
- Unexpected Repairs: Unplanned repairs can be hard on your pocketbook. To get ready, keep up a cash reserve for repairs and emergencies.
- Market Downturns: Real estate markets can fluctuate. Take the long view and be willing to retain your properties in down markets.
- Legal Issues: Seek advice from lawyers on any legal challenges that might arise. A good attorney can help you avoid making costly errors.
Conclusion
So in sum, investing in real estate can be a tremendous generator of wealth and a real way toward financial freedom. So, with some clear levers to work on, you can begin your journey to being a successful investor in real estate by taking control of the path that works best for you with the help of this comprehensive guide. Don’t forget to learn, have clear goals, and form a strong support team.
Call to Action
Begin your real estate experience now! Get our complimentary real estate investment checklist and subscribe to the newsletter for more tips pages and resources!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How much do you need to start investing in real estate?
The minimal amount to begin real estate investing can differ according to the strategy and geographic location.
But with creative financing, that’s not impossible, you can even start investing in real estate with no money down.
2. Is real estate investment risky?
Real estate investing comes with its risks, like any investment. But with the right knowledge, preparation and risk reduction, you can make the downside as small as possible.
3. How long does it take to make money in real estate?
Returns in real estate take time (how much depends on the strategy and the market it is in). But with a well-considered investment, you can begin to see returns in a matter of months to several years.
4. Do I need a real estate license to invest?
No, you do not need a real estate license to invest in real estate. But a license will give you more access and information.
5. What’s the best kind of property for a beginner?
I find a good type for an beginner will depend on their goals, budget, and local market conditions. But for many investors, single-family homes and small multiunit complexes provide an entry point.