Balancing acts between opportunity and obstacle have always been a part of running a small business. In the blaze of the excitement for creating one’s own vision, an entrepreneur still encounters hurdles that, if not addressed, can stall progress.
The subject of Overcoming Small Business Challenges: Trusted Advisory Approaches is a vital one for any business owner serious about sustainability and expansion.
When small business owners start to do what advisors do – providing clarity, direction and confidence – they turn setbacks into stepping stones.
The Small Business Challenge Landscape
Small businesses are the lifeblood of many economies, yet they’re hardly ever a walk in the park. From financing challenges to stiff market competition, those challenges often decide if a company survives or thrives. Some of the problems one might encounter include:
- Limited access to funding.
- Complex compliance with regulations.
- Finding skilled talent.
- Managing cash flow effectively.
- Keeping pace with tech, digital culture and consumer behaviour.
The good news is that trusted advisors—industry veterans offering financial, strategic or operational counsel—can help entrepreneurs turn these challenges into bite-sized portions.
Why Small Businesses Can’t Afford to Ignore Advisory Services
Advice that’s specific to both their industry and their goals is invaluable for any small business. Trusted advisors give you more than advice; they are accountable, offering actionable strategies and risk assessment. This outside view helps prevent small business issues from vanishing without trace.
Entrepreneurs are usually reluctant to hire advisors because they’re too expensive or it means giving up control of their company. However, the truth is that advisory services become partners, providing clarification in uncertain times.
By understanding what advisors care about – from setting goals for realistic budgets to how to scale your programme most effectively – these critical insights pave the way for sustainable growth.
The Big Issues and Advice for Small Business
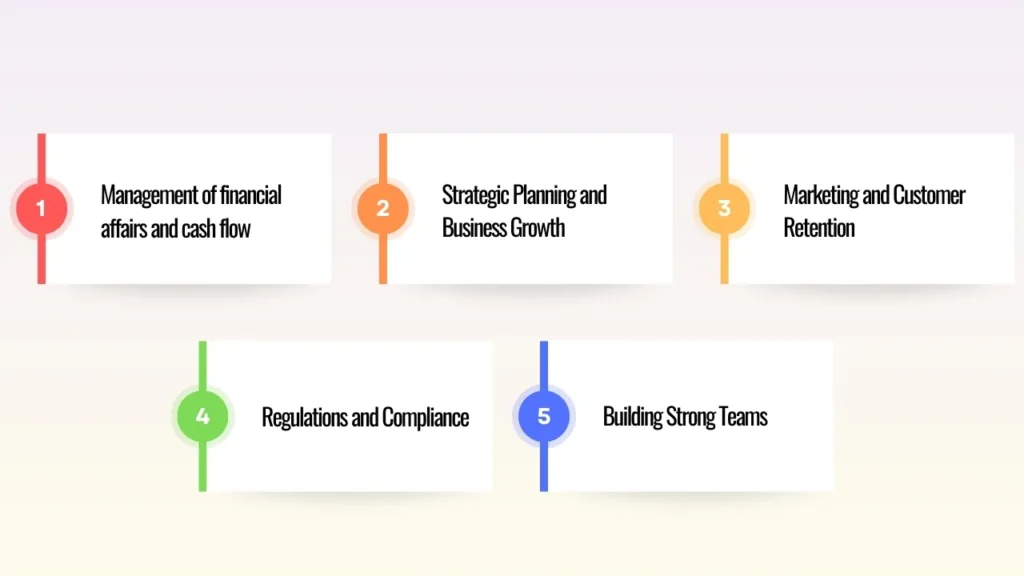
1. Management of financial affairs and cash flow
Cash flow is still one of the top stressors small business owners face. Without a steady supply of cash, daily operations, payroll and investment projects may come to a halt.
Advisory system: Advisors help with rigorous cash-flow projections, managing expenses and creating realistic budgets. They also advise on restructuring loans or accessing alternative sources of financing while preserving liquidity.
2. Strategic Planning and Business Growth
Long-term planning is a drag for many small businesses because what you need right now will always trump the five-year plan. Without that map, scaling a business can seem haphazard.
Advisory system: Strategic advisors create feasible roadmaps in line with the objectives and resources. They’re emphasising market analysis, competitor benchmarking, and goals measurement. For a business that is growing steadily over months or years, this type of vision allows for more seamless expansion and fewer mistakes.
3. Marketing and Customer Retention
It’s a recurring challenge to acquire and keep customers. There are few ways for a small company to make its clout and interests heard above the din when it has larger competitors.
Advisory system: Marketing advisors can guide them to the best channels for outreach, including targeted digital initiatives, customer loyalty and brand building. With targeted marketing spend in lockstep with business goals, the small business will gain recognition and credibility in the marketplace.
4. Regulations and Compliance
Tax laws, labour regulations and company-specific compliances sap time and resources. Owners of small businesses might unknowingly put themselves at a risk.
Advisory system: Legal and compliance advisors enable such systems and make sure documentation, licences and policies are implemented correctly. Their participation helps keep you in line with the local and international rules that greatly reduce your risk.
5. Building Strong Teams
Talent acquisition becomes more complex for small businesses. Competitive wages and/or benefits may not always be possible.
Advisory system: HR advisors share tips to make workplaces over with attractive cultures, non-cash benefits and engaging talent frameworks. Their tactics increase talent retention while managing budgets.
Key Small Business Problems and Management Advice
| Small Business Challenges | Advisory Solutions |
|---|---|
| Cash Flow Shortages | Budgeting techniques, alternative funding, cash tracking |
| Lack of Strategic Planning | Business roadmaps, competitor analysis, scalability plans |
| Marketing Limitations | Targeted digital campaigns, customer loyalty tactics |
| Regulatory Confusion | Tax compliance support, legal structure guidance |
| Hiring and Retention Issues | Employee engagement methods, flexible HR strategies |
The Human Factor of Business Challenges
Behind every small business challenge is human perseverance. Developers frequently mix elbow grease with professional daring. Yet fatigue and decision fatigue can dull the faculties. Outsiders play the role of sounding board – those to be heard off by those who can distinguish fact from emotionalism and prefer rational strategies.
Advisors also bring accountability. Customers commit to action when provided with advisory-based guidance, and execution is faster as they follow through reliably. This human relationship angle sets advisory services apart from more generic advice available elsewhere.
Technology in Small Business Advice
Today’s advisory model combines human expertise and technology. There are other recommended tools for bookkeeping, customer relationship and project management in place to make the process smoother.
For instance, cloud-based accounting systems for small businesses take out all the guesswork and time-consuming transactions that divert you away from your management duties. With the proper combination of technology and advisory input, even the small business can operate like a bigger competitor.
Overcoming Resistance to Advisory Approaches
A lot of entrepreneurs are scared to take in advisories because they believe it’s a critique, not advice. Shifting mindsets is vital. Sustainable advisory strategies should be viewed as partnership — not intrusion.
The Benefits Of Small Business Advisory Services Once you start to see advisory services as an investment in growth rather than a cost, their value becomes clear: to help ensure small business problems never turn into closed-door events.
Unlocking Growth Opportunities
Companies that small businesses have come to love having advisers also gain some protection against risks as well as the ability to find opportunities on offence. Advisors can help identify:
- Untapped markets.
- Expansion via partnerships.
- New product or service lines.
- Financing options beyond traditional banks.
mode and When advisers see these opportunities, the small business that has been in survival mode is now capable of going into growth mode and proving its long-term relevance.
Long-Term Impact of Trusted Advisory
The value of advisory-type work is not just about quick-fix responses. Black writes, ‘Small businesses accumulate more powerful systems, healthier financials and stronger brand recognition over time.’ More importantly, the owners are no longer stressed and can concentrate on innovation and customer satisfaction.
Advisory solutions won’t ensure a smooth ride, but they’ll greatly reduce the turbulence. Each small business owner that acquires specialized advice gets saved from unnecessary losses and paves the way to stable development.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are some typical small business challenges?
The biggest difficulty points are shortages of cash flow, lack of scalability, compliance with regulation, talent retention and too narrow a reach of marketing.
2. How does an advisor finance a small business?
Advisers provide assistance in budgeting, cash flow management, and investigating funding options, as well as minimizing financial risk through ongoing monitoring.
3. Can advisory models help small businesses grow?
Yes, advisors can help to make expansion efforts more organised and realistic by offering strategic planning, competitor analysis, and resource allocation.
4. Advisory services for small businesses – Is it expensive?
Cost ranges vary, but most advisory services peg their fees based on the size of the business. For a price, many owners think the return on investment is worth it.
5. How does technology help you tackle small business challenges?
When technology is paired with advisory oversight, it assists in creating efficiencies, reducing errors and increasing client relationship through the use of accounting software and CRM applications.