Cross border tax planning can save your business money Knowing how cross border tax planning can save your business some money, particularly if you are doing work in the global marketplace, is important if you want to thrive. Cross border tax planning is about planning how to pay as little tax as you legally have to if your business operates in more than one country.
Cross border tax planning With tax laws varying so much from country to country, effective cross border tax planning can help you reduce your total worldwide tax burden, avoid the double taxation that results from being taxed in multiple countries on the same income and maximize cash flow.
During the course, we will also rely heavily on these particular terms, “cross-border tax planning” and “cross-border and tax planning,” because they are essential to understanding the subject! Let’s start by looking at why businesses need this specialized tax planning when it comes to crossing borders.
Cross Border Tax Planning Makes a Difference – Here’s Why
International businesses face challenging tax systems. Every country has its own tax system, tax rates, reporting obligations and compliance regulations. Without diligent cross-border tax planning, corporations can face:
- Having money taxed twice: double taxation of the same source of income
- Tax credits, or treaty benefits overlooked
- Not fully compliant with local tax laws
- Facing penalties or costly audits
At its most basic level, cross border tax planning means arranging your business and finances in such a way that you obey the law and keep taxes to an absolute minimum. This forward-looking strategy enables risk management and sustained growth across various markets.
Summary of Tax Implications Associated with Cross-Border Tax Planning
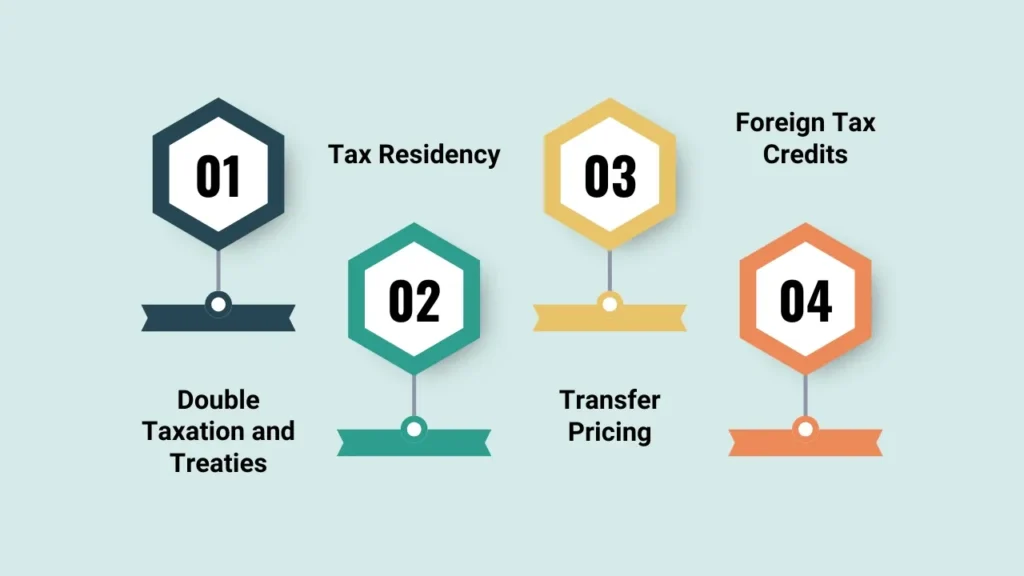
1. Double Taxation and Treaties
The concept of double taxation is based on two countries both asserting jurisdiction to tax the same income. To avoid this situation, many countries have entered into double tax treaties or Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs).
These agreements determine which country has the right to tax and generally decrease the amount of withholding taxes requested on payments between one country and another, including dividends, interest, or royalties.
2. Tax Residency
Deciding tax residency is important because a business and you as an individual have tax regulations for these entities, respectively, that are based on where they reside. Countries have different regulations—either concerning physical presence tests, permanent home criteria or economic ties.
3. Transfer Pricing
The transfer pricing rules essentially determine the price between goods and services sold by entities within the same organization but which are located in different countries of operation. The fair market valuation of such intercompany transactions is essential to be legally compliant and tax efficient.
4. Foreign Tax Credits
Many countries permit taxpayers to offset foreign taxes paid against domestic tax liabilities in an effort to alleviate double taxation.
Strategies that Will Maximize Cross Border Tax Planning
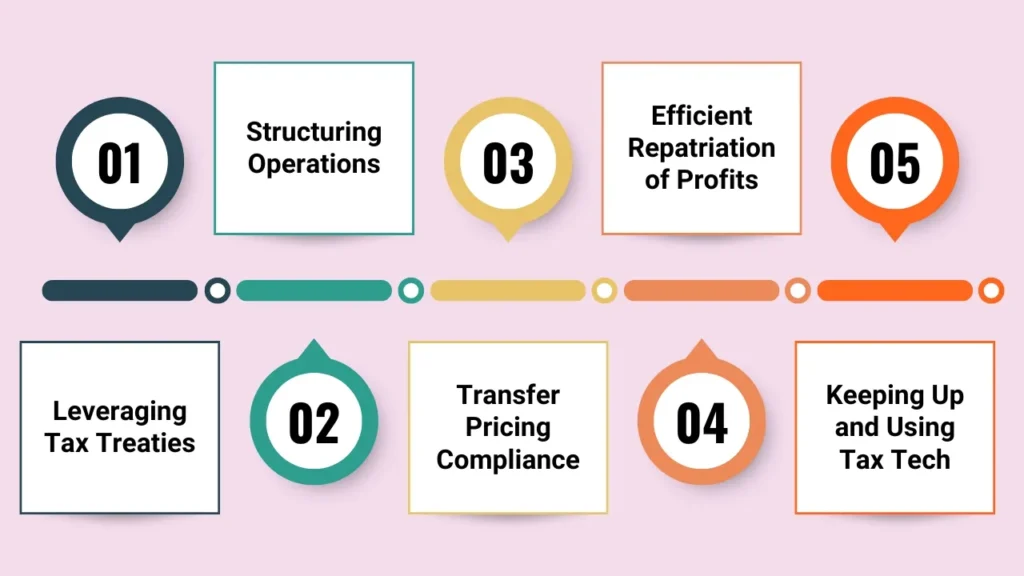
1. Leveraging Tax Treaties
Recognize and apply relevant tax treaties to enjoy lower withholding rates and avoid double taxation. For instance, the US – Canada tax treaty provides reduced withholding on cross-border dividends and tie-breaker provisions for dual residence.
2. Structuring Operations
Look at your corporate structure—the use of subsidiaries, holding companies or branch offices in tax-friendly locations can reduce the fundamental rate of taxation.
3. Transfer Pricing Compliance
Draft effective transfer pricing plans and documentation to meet the stringent adherence to international regulations and prevent disputes with tax authorities.
4. Efficient Repatriation of Profits
Make repatriation of income back to the parent company from foreign subsidiaries as tax efficient and cash optimal as possible.
5. Keeping Up and Using Tax Tech
Stay current with evolving international tax regulations and use technology solutions to ease cross border compliance.
Some General Inputs to Cross Border Tax Planning:
| Element | Description | Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Double Taxation Treaties | Shared tax authority agreements minimizing double taxation | Ensures not taxed twice for same income |
| Tax Residency Rules | Rules defining residency of a business or individual for taxation purposes | Determines appropriate taxing jurisdiction |
| Transfer Pricing | Specifications preventing mispricing on related party international transactions | Compliance and optimization |
| Foreign Tax Credits | Credit funding for foreign taxes paid against local tax | Liability mitigation |
| Transfer Planning | Plans to repatriate earnings with minimum withholding to home country | Cost savings, improves cash flow |
Typical International Tax Planning Obstacles
- Complexity of varying tax laws
- Navigating multiple compliance deadlines
- In coordination, linguistic and cultural barriers
- Unforeseen developments in international tax laws and rules
- Documentation and data across jurisdictions
To solve these challenges, companies frequently turn to expert tax advisors and software developed for managing international taxes.
Final Words
The ability to understand how and why cross border tax planning can save your company money is a crucial part of staying one step ahead in the global economy. If you learn how tax treaties, residency rules, and transfer prices work—and use credits appropriately—then your company can minimize its tax burden in all other countries where it operates.
It is no longer enough for cross border tax planning to simply ensure compliance; it must be viewed as an advantageous means of facilitating expansion, enhancing cash flow and also preserving long-term wealth.
Keep yourself informed and consult your tax advisor in time to coordinate with evolving global positions on cross border tax planning.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is cross-border tax planning?
Cross border tax planning refers to the practice of managing tax responsibilities when doing business in more than one country, trying to minimize taxes while respectig each country’s laws.
2. How does cross border tax planning assist in the removal of double taxation?
It does this by resorting to double taxation treaties and foreign tax credits that prevent the same income from being taxed in two places.
3. Why is the understanding and application of transfer pricing in cross-border tax planning very important?
Transfer pricing—used to ensure transactions between related companies from different countries are appropriately priced in order to avoid facing a tax penalty.
4. What is the impact of cross border tax planning on cash flow?
Yes, it increases available cash flow… by managing withholding tax, maximizing profit repatriation and minimizing overall tax exposure.
5. Should companies consider getting professional advice in cross border tax planning?
Due to the complicated and ever-changing nature of international tax regulations, it is strongly advised that professional taxation advice be sought.