In this ever-changing world of finance, among the waves and shifts that we are experiencing in today’s economy, it is that much more important to consider balancing technology and empathy in debt collection. While technology achieves efficiency on the volume end, empathy keeps debtors treated with compassion and decency.
This combination of elements is revolutionising the debt collection industry, achieving better recovery rates with a far more humane approach to the borrower.
This post investigates the opportunity to remake the way debt is collected in a digital age by integrating cutting-edge technology with empathetic consumer interaction and how combining service and empathy could pay dividends for lenders and borrowers alike.
Understanding the Need for Balance
The nature of debt management lays itself firmly at the other side of the spectrum with conflict, stress and cold-faced procedure. But, as interventional specialist Lydia Mayer Jeraj noted during the call, as consumers grow savvier and regulations tighten on robocalls, going all mechanical or “scorched earth” could come back to bite you by sullying your reputation and slashing down recovery.
Conversely, depending on empathy only – without effective technology enabling processes – can slow collections and add to wasted operational hours.
This is where integrating technology with sensitivity becomes extremely crucial. Where technology automates standard communication and can segment debtor profiles and predict repayment behaviour, empathy humanizes the messages and dials up cooperative goodwill.
How Technology Enhances Debt Collection
Today’s debt collection technologies span features such as data science applications, automated systems, omnichannel connectivity solutions and the use of predictive modelling.
- Automation decreases the manual workload by managing mundane tasks like reminders, status updating and simple queries.
- Analytics and prediction models help in prioritising efforts by identifying buyers most likely to repay.
- Omnichannel platforms allow engagement on the channel of choice – phone, SMS, email or web portals – giving borrowers a way to engage the way they want.
- Real-Time Monitoring monitors debtor activity and progress with payments while strategies change on the fly.
Thanks to these technological innovations, you can streamline your workflows, better segment your debtors, and intervene in a timely manner with precise actions that increase recovery rates.
The role of Empathy in the World of Debt Collection
While automation speeds up processes, empathy slows them down. It takes compassion and flexibility to understand a borrower’s situation, whether that someone is experiencing financial challenges, health troubles or job loss. Empathetic communication involves:
- Attentive listening and acknowledging personal difficulties.
- Making personal payment plans or temporary arrangements.
- Respectful language, i.e., free of intimidation or threats.
- There is value in discussing repayment options and consequences.
Empathy in debt collection doesn’t mean being soft; through the approach of collaboration & trust, we can ensure debtors are actively involved in any type of solution to resolve their debts.
Balancing Technology and Empathy Implementation: Best Practices
Balancing Technology and Humanity It’s all about a synergistic approach in which technology enables people-led engagement, instead of the latter being replaced by it.
| Aspect | Technology Role | Empathy Role |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Automated reminders, omnichannel messaging | Tone customization, personalized outreach |
| Debt Segmentation | Predictive analytics to identify priority cases | Understanding financial context for flexibility |
| Payment Plans | Digital self-service portals with flexible options | Human negotiation for hardship accommodations |
| Compliance | Automated regulation checks and audit trails | Fair treatment and transparent disclosures |
| Data Use | Analyzing debtor behavior and payment history | Respecting privacy and sensitive data handling |
The table below shows how these two approaches reinforce each other to form a more powerful and borrower-friendly system.
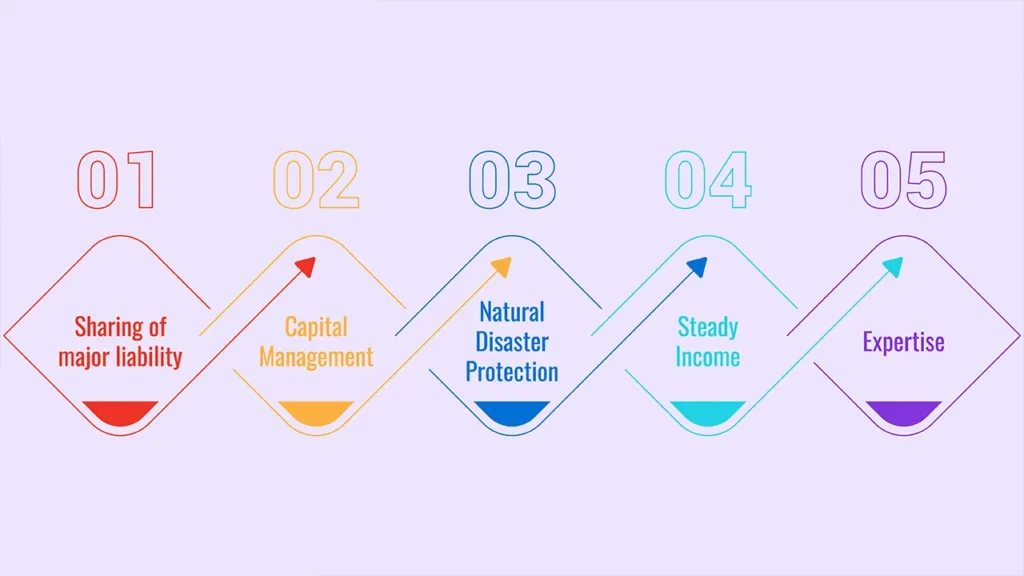
Benefits of Competition Between Empathy and Technology

- Better recovery: Targeted and data-driven approaches to customer-specific engagement can lead to higher rates of recovery.
- Fewer Complaints and Legal Liabilities: Courtesy along with Conformity diminishes complaints and legal actions.
- Favourable Brand Perception: Ethical collections promote goodwill, leading to subsequent borrowing and loyalty.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation frees resources from mundane responsibilities; empathetic negotiations prevent costly escalations.
- A Better Borrower Experience: When borrowers feel respected and are able to be heard, engagement increases and stress decreases.
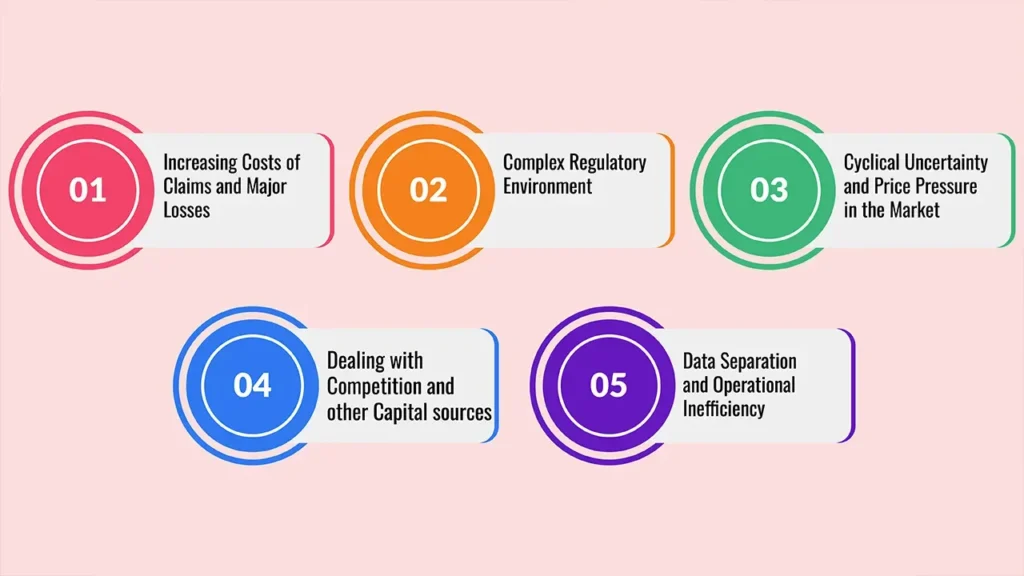
Challenges to Achieving Balance
Despite benefits, organizations face challenges:
- Technology can over-automate and lead to robo- or unemotional communication.
- Empathy is an issue in both human agents who might be inexperienced and slow, possibly leading to inflated labour costs.
- Privacy restrictions confine the level of personalization possible.
- Adapting To Constant Change Staying compliant in more than one regulatory jurisdiction requires constant adjustment.
- Integrating tech and human workflows can be tough.
- Tackling these challenges requires continued training, careful selection of technologies and good governance.
What the Future Holds for Debt Collection: A Human-Tech Approach
Technology and empathy counterbalance will increase as a trend. Upcoming innovations like intelligent automation, real-time data analytics and sentiment analysis will allow debt collectors to make individualised treatment at scale a reality.
Agents will be better coached when technologies can pick up on emotional triggers, and the intent to pay will also be taken into account. Borrowers are now looking for the level of respect and convenience they receive in their digital retail experiences or from banks.
Preferable debt collection agencies of the future will be those that leverage responsible use of technology to provide transparency, flexibility and engagement.
Final Words
Balancing debt, debt collection and balancing technology in today’s environment requires a smart blend of machines and human touch. With technology serving as a means of facilitating, rather than replacing, humanity, the arms race between creditors and debtors evaporates to create more efficient and effective debt-collection processes for both parties.
Companies that adopt this balanced approach can deliver superior financial planning results, remain in regulatory compliance, and build a portfolio of long-term borrowers through 2025 — and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why does technology matter in debt collection?
Technology automates a lot of the same borrowed but old methods, bringing greater accuracy in contacting debtors down to multi-channel communication and making collections more efficient and scalable.
2. How does empathy help in debt recovery?
Empathy builds trust and cooperation by recognizing a debtor’s financial status and personal circumstances, facilitating payment arrangements that both parties can consent to, and lowering animosity.
3. What is balancing technology in debt collection?
It’s how you use tech tools, such as automation, analytics and omnichannel platforms with a human focus – respectful communication among them – or offerings like personalized payment options, to maximize those results.
4. Is too much technology bad for debt collection?
Yes, overly automating can bring your communications to a point where they feel unpersonalized and mechanical, which might turn the debtors off making it less effective.
5. What’s the role of compliance in balancing the technology and empathy scale?
Compliance ensures that all debt collection activities comply with the law, ensuring rights of debtors and protecting organizations from being exposed to legal risks in addition to receiving fair treatment.