In a highly convoluted insurance landscape, companies are exposed to huge risks that may ultimately compromise their sustainability. That is where reinsurance comes in.
Reinsurance is how insurers can take some of the risk they have on their books and pass it on to another company to ensure that that insurer has a stable balance sheet and can maintain solvency so customers can continue to count on a certain level of security.
Knowing which reinsurance strategy is the right fit is key for insurers who want growth and sustainability in this new economic and regulatory environment we all live in today.
This article looks at the basics of reinsurance, critical components in developing a successful reinsurance strategy, insurers’ options to choose from when developing such strategies and tips on how they can begin crafting a strategy tailored to their own particular challenges.
Understanding Reinsurance
Reinsurance is insurance for the insurance companies. Like individuals and businesses that buy insurance to cover financial losses from unexpected disasters, insurance companies themselves buy protection on the market – reinsurance.
This serves to more evenly distribute risk across the industry so that no single insurer is holding an unmanageable burden.
An intelligent reinsurance tactic helps insurers in:
- Protecting against catastrophic losses.
- Being in solvency and having sufficient capital.
- Promoting financial stability by controlling exposure.
- Enabling consistent underwriting practices.
Why a Reinsurance Strategy Matters
The selection of the proper reinsurance strategy has a bearing on all parts of the insurance business. Without it, businesses can go bankrupt during major catastrophes, lose competitiveness or spend years trying to satisfy regulatory mandates. Effective planning supports:
- Long-term profitability.
- Capital relief and liquidity management.
- Protection from systemic risks like natural disasters or pandemics.
- Expanded underwriting capacity to write more business with confidence.
For this reason, there is no alternative to this reinsurance approach, and it must be seen as the basis of a sustainable insurance business.
Types of Reinsurance
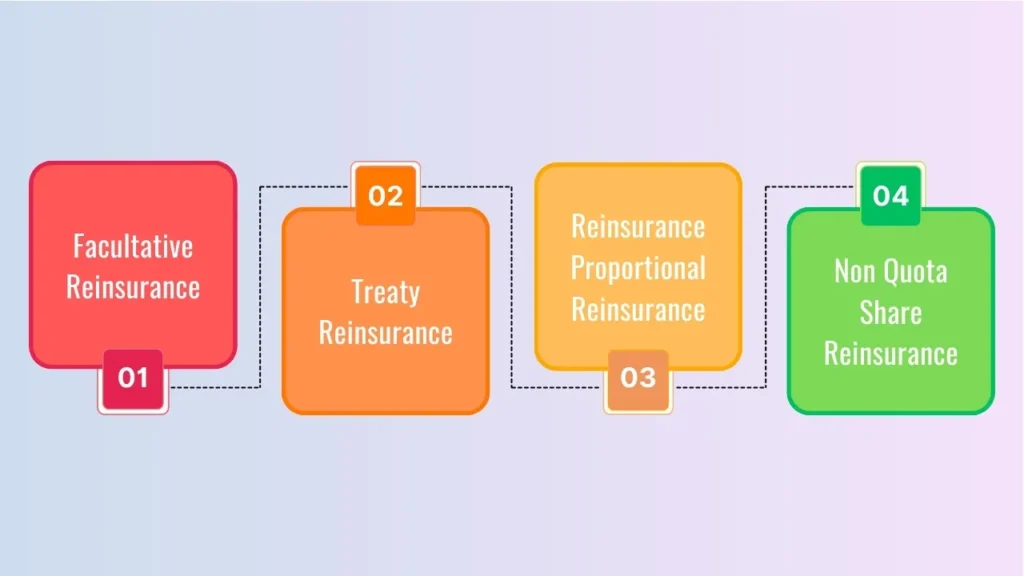
Types of reinsurance and understanding it Before we design a strategy, insurers need to know distinct types of reinsurance.
- Facultative Reinsurance: Reinsurance of a specific risk or policy on an individual basis, designed for large or unusual exposures.
- Treaty Reinsurance: An entire book of business is reinsured under a single contract providing permanent protection.
- Reinsurance Proportional Reinsurance: the reinsurer shares premiums and losses at an agreed portion.
- Non-Quota Share Reinsurance: The reinsurer is liable for losses above a specified value, often referred to as the retention and typically used on catastrophe excess-of-loss reinsurance treaties.
Determining Factors of a Reinsurance Strategy
Successful implementation of a reinsurance strategy requires assessment and consideration of several factors:
1. Risk Profile
A portfolio’s nature must be taken into account by any insurer. For example, a company that underwrites property insurance in disaster-prone regions will need robust catastrophe reinsurance.
2. Regulatory Requirements
Solvency Capital Standards are established in every jurisdiction. A reinsurance plan should be in accordance with these rules to be compliant.
3. Capital Management Goals
Reinsurance should be used by companies to achieve the most efficient capital structure, allowing surplus funds to be released and enabling growth without gross loss.
4. Market Conditions
Reinsurance pricing and capacity are based on world events, interest rates, and catastrophe history. A mechanism should be able to accommodate this variability.
5. Long-Term Strategic Objectives
Insurers are also seeking disparate outcomes in the market as well: some want to grow aggressively by writing more business, while others are focused on stable profitability. The appropriate reinsurance programme will be in line with these objectives.
Methods for Constructing a Reinsurance Program
Selecting a reinsurance approach is about trade-offs between risk tolerance, cost and strategic direction. Some commonly adopted approaches include:
- Conservative Protection: Based Splits its focus on reducing volatility and preserving capital.
- Traction: There are several examples where a reinsurance strategy allows growth in underwriting capacity and new markets.
- Hybrid response: security, combined with growth; short-term resilience in equilibrium with long-term expansion.
Common Examples of Reinsurance Practices
| Reinsurance Approach | Key Features | Advantages | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative Protection | High reliance on reinsurance, low risk retention | Capital stability, reduced financial strain | Insurers prioritizing solvency and risk avoidance |
| Growth-Oriented | Higher retention with selective protection | Increased capacity, premium growth | Expanding insurers entering new markets |
| Hybrid | Balanced use of proportional and non-proportional structures | Protection with growth flexibility | Companies seeking resilience and expansion |
Movements to Creating the Optimal Reinsurance Program
- Perform Risk Studies – Review exposure profiles, catastrophic risks and claims experience.
- Work with Reinsurance Brokers – Brokers offer market intelligence and access to a multitude of reinsurers.
- Risk appetite and retention limits – Specify the level of loss the insurer is willing to sustain.
- Assess Cost to Benefit – Check how much do you pay against the protection offered.
- Choose the right model – proportional, non-proportional, or a blend that’s best for your aims.
- Review and Adjust Regularly – A reinsurance plan should live and breathe as risks change.
Common Challenges in Reinsurance Strategy
- Reinsurance costs increasing from weather or lack of market – WACC premium
- Regulatory disparities in regions with different solvency requirements.
- Unpredictable Disastrous Trend Downflow is impacted by global warming and geopolitical risks.
- RICO Reinsurance When a reinsurer defaults on its obligations.
Such challenges underscore the critical importance of continuing monitoring and key partnerships with approved reinsurers.
Best Practices for Reinsurance Strategy
- Keep up robust data analytics to stay on top of changing risk.
- Participate with multiple reinsurers to prevent concentration risk in a single reinsurer.
- Weigh immediate cost savings against long-term resilience.
- Integrate stress testing with decision-making and scenario modelling.
- Provide transparency and consistency between the underwriting scope and reinsurance strategy.
Future of Reinsurance Strategy
The reinsurance environment is evolving rapidly, driven by climate change, digitalisation and global economic instability. Parametric reinsurance, where pay-outs are based on pre-defined indices rather than loss assessment, is one of a range of innovative products that insurers are turning to. What’s more, capital market plays such as catastrophe bonds are increasingly part of larger reinsurance.
The Winners of Tomorrow’s Insurance Industry Will Be Those Who See Reinsurance Strategy Not as a Cost Management Exercise, but as an active risk management lever tuned to the long term.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the ultimate goal of a reinsurance programme?
The ultimate aim is to shield insurers from significant adverse variance, maintain solvency and foster predictable growth.
2. What is the difference between reinsurance and insurance?
Insurance provides protection to businesses and individuals; reinsurance protects insurance companies by dispersing their risk.
3. What sort of reinsurance works best for catastrophe cover?
Non-proportional covers, especially excess-of-loss reinsurance, have become most common for cat events.
4. What is the frequency insurers should quantify their reinsurance strategy?
Once a year is good, but to be better, do it after each major regulatory change.
5. Can reinsurance help carriers enter new markets?
Indeed, growth reinsurance positions insurers to expand underwriting capabilities and enter new territories with a manageable level of risk.

Leave a Reply