One investment stands out in a world that is changing because it continuously offers high returns in terms of quality of life, personal and professional fulfilment, and financial returns. That investment? Education.
In this article, we will be discussing “Funding Education as an Investment in the Future” – why it makes financial sense to spend strategically on education, the many aspects of the ROI it provides and how to go about it to get the most out of the exercise.
If you get that education is an investment in your child’s future and your finances, you can make solid financial planning.
1. Why Education is a Priceless Investment
Beyond Degrees: Understanding the True Value of Funding Education as an Investment in the Future
- Human capital development: Education/schooling is one of the ways that develop human capital or people’s skills and how they use their skills to become productive and achieve economic success.
- Returns in the long run: Unlike physical assets, the returns on education increase over the years and are something that gives a return beyond the initial cost.
- Inflation-Resilient Asset: A body of knowledge and skill is not subjected to inflation; in fact, at an economic progression stage, it can become more valuable.
- Non-monetary: Education encourages critical thinking, the ability to solve complex problems, adjust to change, and grow as a person, thus enhancing their lifestyle.
2. Education’s Measurable Returns on Investment
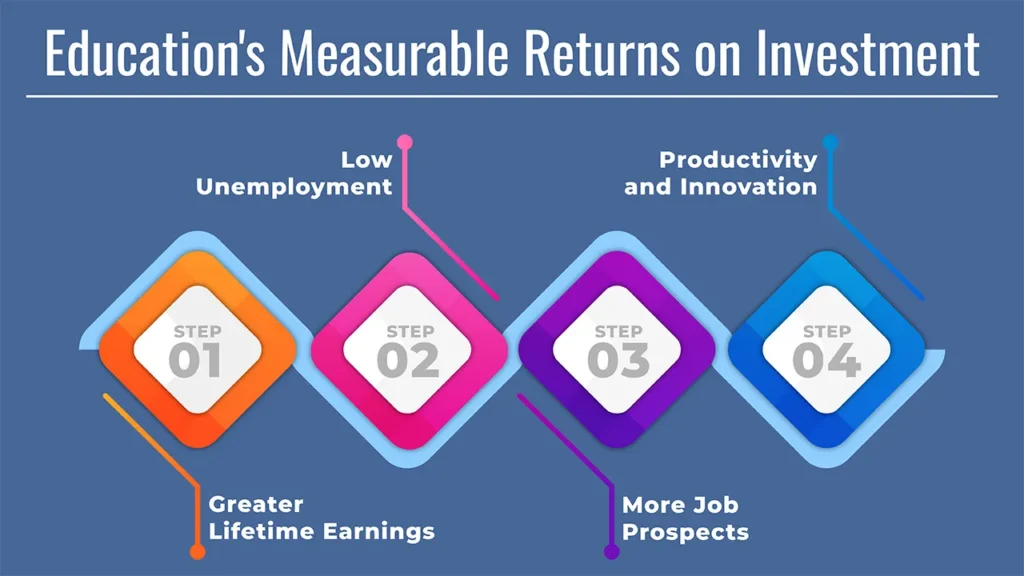
Economic Financial Gains: Increasing Earning Power and Financial Stability
- Greater Lifetime Earnings: Research indicates that there’s a strong relationship between your level of education and the amount of money you will make over your lifetime, and those with more advanced degrees have the potential to earn substantially more.
- Low Unemployment: It is not a surprise, then, that they are often not unemployed and more secure in times of economic downturn.
- More Job Prospects: With an education, you have more job opportunities, which means more satisfying jobs – and therefore a better quality of life.
- Productivity and Innovation: Benefit for Society An educated workforce is the root of developing social capital, which results in faster economic development.
The U.S. Bureau of Labour Statistics (BLS) consistently publishes data demonstrating the correlation between higher education levels and increased earnings, along with lower unemployment rates. Explore the latest data from the BLS on Education Pays.
3. The Non-Financial Margin of Investment in Education
Beyond Money: A Wealth of Non-Financial Benefits
- Deeper Critical Thinking or Problem Solving: Education pushes us to improve our cognitive abilities and solve challenging issues.
- Personal development: Education has an impact on personality, confidence and adaptability in the changing world.
- Better Health: Participants in higher education programmes generally practice healthier lifestyles, and volunteering leads to enhanced health.
- Increase in Civic Participation: More educated people are more likely to participate in community and democratic processes which make societies stronger.
- Intergenerational Mobility: Education can break the generational cycle of poverty & improve family prospects, opening the way for future generations.
- Network and Social Capital: The exposure to varied networks and opportunities made available thanks to thousands of alumni can result in better career opportunities and a happier life.
4. Strategic Choices for Financing Your Investment in Education
Planning Your Investment: Key Financial Strategies
- Real Estate Investing: Key Financial Strategies For Planning Your Investment
- Early Saving and Compounding: The value of starting early with investments specifically targeted for education in tax-sheltered accounts (529s, RESPs) or general diversified mutual funds.
- Budgeting and Priorities: Be deliberate about how you spend on education. Your budget and funding strategies should translate that education is a priority.
- Diverse Investment Devices: Utilising a blend of growth (shares) and defensive (fixed interest) assets that are appropriate for your education goals time frame.
- Hunting for Scholarships and Grants: Use merit-based or need-based aid as a means to cut out-of-pocket costs and save on tuition.
- Smart Borrowing (Educational Loans): If you need loans, know the differences in interest rates, repayment terms, and possible government subsidies in order to minimize your financial burden.
- Part-Time Work or Internships: Support both getting some experience and covering bills with a part-time job or part-time role.
5. Optimising Your Return on Investment in Education
Beyond Tuition: Making the Most of Your Educational Journey
- Strategic Choice of Fields: Select fields in which the job markets are most robust and prospective growth opportunities are strong.
- Networking: Make friends with faculty, students, and professionals so you can cultivate great relationships.
- Put it all to practice: intern, co-op or conduct research to get hands-on, practical experience.
- Lifelong learning: Focus on the need for ongoing learning and reskilling in a rapidly changing world to be competitive.
- Take Advantage of Career Services: Use your college’s resources for job placement and career assistance and make the most of post-education opportunities.
Conclusion
Investing in education is the best thing we can do for our country’s financial health and workforce. This is a strategic choice that enhances the individual, the economy and society as a whole. We have to look at each rupee or dollar or pound spent on education as a lifelong appreciating asset towards growth and prosperity.
Call to Action
Motivate readers to begin planning for their (or their child’s) education today, because it is one of the wealthiest investments they can ever make.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Is education still worth the investment, now that the costs and student debts are mounting?
Yes, although it seems costs continue to increase, there is no shortage of empirical research showing higher ed offers higher lifetime earnings, lower unemployment rates, and more economic mobility. The difference is to plan and finance strategically so that debt can be handled in a thought-out manner.
2. What is the “return on investment” of education?
There are many dimensions in the ROI of education. Quantifying this economically is in the form of improved lifetime earnings and career opportunities.
And on intangibles, it contributes to improved critical thinking, personal development, better health and civic engagement, all of which contribute to a life well lived.
3. Are vocational training and skill-based certifications also considered good investments?
Absolutely. Vocational education and skills-based certifications in today’s labour market can yield excellent returns and lead to well-paying, in-demand jobs with shorter training periods and oftentimes, with lower costs, compared to traditional degrees. They are very profitable investments in human capital.
4. Is there a way to reduce the debt impact when borrowing for education?
Avoid debt by saving early and often, investigating tax-advantaged education savings plans, applying for scholarships and grants, looking into more affordable schools, and if borrowing is necessary, knowing what you are borrowing and making a plan/payoff schedule.
5. Should I invest in my child’s education even if they might not pursue a traditional career path?
Yes, education as a whole arms people with critical thinking skills, problem-solving and flexibility—skills that certainly aren’t unique to the unconventional career path.
Whether in person or online, investing in their learning and development means investing in their potential and capacity to add value in the future.